Do Password Managers Track My Information?
6 min read by Bogdi
published 5 years ago, updated 4 years ago
Password overload: it’s unavoidable in this day and age. With so much business conducted online, everything, from buying groceries to subscribing to a new television streaming service, requires a username and password to access. As the sheer volume of passwords is not possible to remember anymore, it can be helpful to use a password manager.
Password managers, in addition to keeping track of your username and password for each site or app to which you are subscribed, also help keep safe information such as security questions, credit card numbers, and PINs.
While it can be scary to trust all of your important information to a single source, password managers are typically much safer than trying to remember all of your passwords separately. Reputable password managers use the highest level encryption that can take hackers decades --if not a lifetime-- to crack. In addition, they use a technique called “zero knowledge”, meaning that while the password manager knows your information, the entity that operates the manager does not.
Why Should You Use a Password Manager?
There are a number of reasons to use a password manager, all of which center around the issue of password overload.
With so many websites requiring usernames and passwords to access, it is nearly impossible to create unique passwords for each that meet the criteria for a strong password:
- Long in length (the longer, the better with password creation)
- No words that can be found in the dictionary
- No personal information, such as date of birth or anniversary
- Random mix of letters, numbers, and special characters
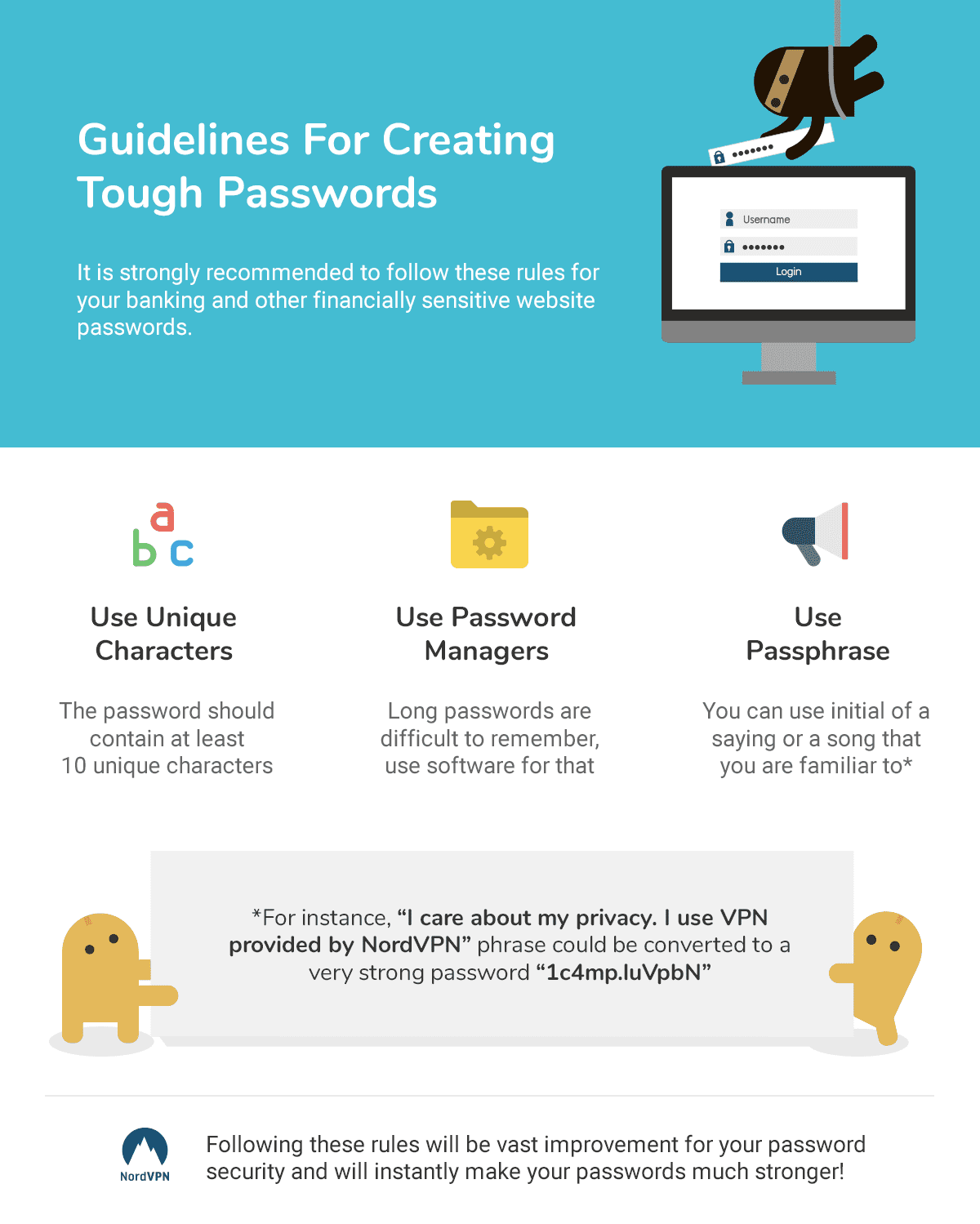
As memorizing unique passwords that contain all of these characteristics is essentially impossible, people often fall into the habit of using simple passwords that are easy to remember. It may surprise you, but the most common password in the world is “password”.
As you can see, this is an easy password for hackers to guess. What’s more: as most people use the same username and password combination across multiple platforms. Once hackers have successfully ascertained your login information for one site, they can quickly run that information across a multitude of common platforms and gain further access to your sensitive information.
Therefore, password managers serve as a solution to this problem. Password managers allow you to create unique, highly complex passwords for each website or app that you use and encrypt these passwords, storing them in a localized or cloud-based server. When you need to login to a specific site, the password manager then populates the necessary fields from the information stored in its servers for that particular site, giving you access to your content.
Is My Information Safe on a Password Manager?
While there are no 100% guarantees when it comes to cybersecurity, password managers are close.
By using a zero knowledge protocol, the entity that operates your password manager has the ability to prove that they know your password without actually knowing your password. While the entire encryption theory behind zero knowledge is too complicated to outline in this article, zero knowledge protocols ensure that even if the entity that operates your password manager is hacked, the hackers would still not have access to your information, as the entity itself does not know the specifics of the information it has.
If you create an extremely complex, unique password for a site and save it to your password manager, you are likely to forget it in a matter of seconds, if you do not write it down. Therefore, once your password is saved to your password manager, the only entity in the world that knows the password is the password manager itself. This makes your information secure.
One of the best ways to think about a password manager is to consider the “passwords” features on your smartphone. When entering your login information to a new site, you may be asked if you want to save this information to “passwords”. If you have chosen a sufficiently strong password, the only way to access your accounts would then be to provide your fingerprint, which is in itself unique, ensuring the security of your information.
Tips for Maximizing Security with a Password Manager
Although password managers are a secure means of protecting your personal information, they are not completely infallible if certain safety precautions are not taken. Therefore, consider the following pieces of advice to ensure that the integrity of your password manager is never undermined.
Choose a Maximum Strength Password for the Password Manager Itself
Although your password manager will be protecting dozens, if not hundreds, of your complex passwords, you must login to the password manager itself in order for it to access your sites.
While your fingerprint is your unique password for the manager on your smartphone, you will need to choose a traditional password for using your desktop or for those phones that do not have finger or face recognition technology.
It can be a disaster if a malicious entity were to gain entry into your password manager, as they would have access to all of your unique login and personal information. Therefore, it is critical that you make a maximum strength password for the manager itself.
Forgetting this password will be inconvenient, as you will then be forced to go and reset each password that is protected by the manager. As such, it is good to write down the password somewhere and hide it in a secure place that you will not forget.
Only Use Your Password Manager on Trusted Devices
Although the encryption used by password managers makes it nearly impossible for hackers to access your personal accounts, the device you are using may not be sufficiently secure from cyber threats, putting the password for your manager a risk.
For example, if you are using a public computer that is infected with malware and attempt to login to your password manager, the malware may have the ability to read every password that is used on the device. Then, by logging into your password manager, the hacker would have access to all of the information listed in the previous section.
Therefore, when using your password manager, it is best to only use it on your personal devices or devices that have strong anti-virus and anti-malware software in place.
Do Not Use the Password Managers Offered as Browser Extensions
These password managers are, basically, browser extensions connected to a server. This means they have no desktop application. You just install them from the Chrome Webstore or Firefox Extensions website.
When choosing a password manager, it is best to avoid options that are offered as an extension on your web browser. Multiple severe bugs were found in these applications over the years.
Browser extensions have a built in communication channel (or API). They are built to be able to communicate with a webpage. This, unfortunately, also means that malicious websites can try to extract your passwords.
Therefore, choosing a desktop-based password manager is a safer option, as hackers will need access to your specific device before a security breach is even possible. This is why the password manager on your smartphone is secure: hackers need both your device and fingerprint to access the manager. This combination will be nearly impossible to obtain.
Your password manager is desktop-based if you can see it in the list of installed programs.
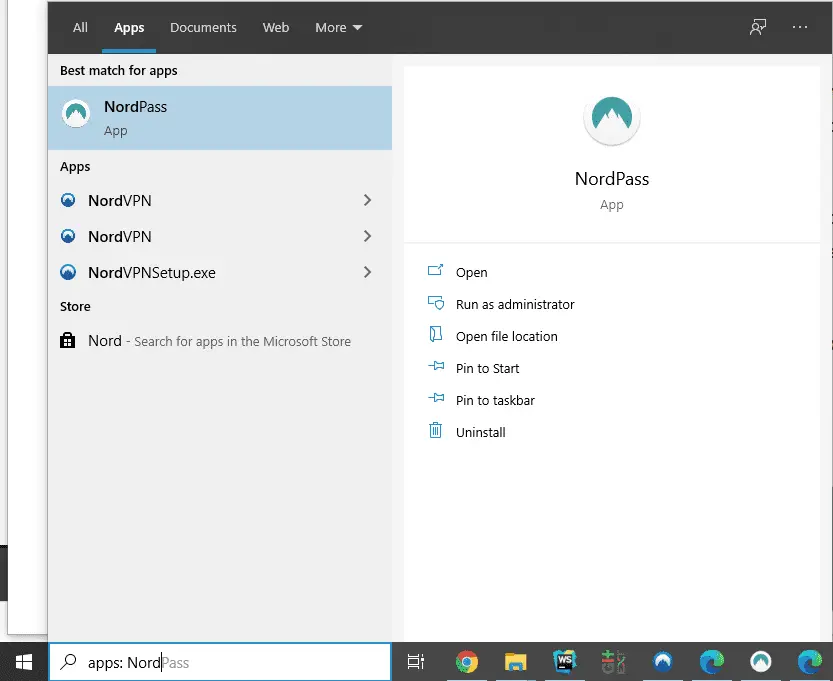
Conclusion
In addition to saving your username and password information from numerous websites, password managers also help protect other sensitive information, such as PINs, credit card numbers, and security questions.
Although it may seem scary trusting one source with all of your sensitive information, the zero knowledge protocols employed by password management software ensures that no entity besides the manager itself knows your information.
When using password managers, be sure to choose a trusted, desktop-based option and secure it with a maximum-strength master password.
Share this with your friends
Related Articles
Here are some articles you might be interested in:
What questions do you have?
I make sure to answer them as soon as possible!
- Copyright © 2020 YOU are safe online.
- All Rights Reserved.
